الضفدع الثاني
(بالتحويل من Beta Ceti)
| الضفدع الثاني | |
|---|---|
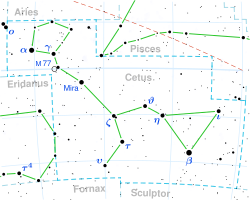
الضفدع الثاني في كوكبة قيطس (β)
| |
| معلومات الرصد حقبة J2000 اعتدالان J2000 |
|
| كوكبة | قيطس |
| مطلع مستقيم | 00سا 43د 35.37090ث[1] |
| الميل | –17° 59′ 11.7827″[1] |
| القدر الظاهري (V) | 2.02[2] |
| الخصائص | |
| نوع الطيف | K0 III[3] |
| U−B مؤشر اللون | +0.88[2] |
| B−V مؤشر اللون | +1.01[2] |
| نوع التغير | Rotationally |
| القياسات الفلكية | |
| السرعة الشعاعية (Rv) | +12.9[4] كم/ث |
| الحركة الخاصة (μ) | +232.55[1]+31.99[1] |
| التزيح (π) | 33.86 ± 0.16 د.ق |
| البعد | 96٫3 ± 0٫5 س.ض (29٫5 ± 0٫1 ف.ف) |
| القدر المطلق (MV) | –0.13[5] |
| تفاصيل | |
| كتلة | 2.8[6] ك☉ |
| نصف قطر | 16.78 ± 0.25[7] نق☉ |
| إضاءة | 139.1 ± 7.0[7] ض☉ |
| جاذبية سطحية (log g) | 2.7[8] سم.غ.ثا |
| درجة الحرارة | 4,797[8] ك |
| معدنية [Fe/H] | –0.09[8] dex |
| سرعة الدوران (v sin i) | 18[9] كم/ثا |
| عمر | > 1[10] ج.سنة |
| تسميات اخرى | |
| Deneb Kaitos, Diphda, Difda al Thani, Rana Secunda, 16 Cet, BD–18°115, GCTP 134.00, Gj 31, HD 4128, هيباركوس 3419, HR 188, SAO 147420.[11] | |
| قاعدة بيانات المراجع | |
| سيمباد | بيانات |
| ARICNS | بيانات |
| تعديل مصدري - تعديل | |
أو بيتا القيطس Beta Ceti اسمه التقليدي Diphda مشتق من الاسم العربي وهو نجم في كوكبة القيطس.
ينتمي إلى الفئة الطيفية بين G وK وبالتالي هو نجم مصفر ابرد نوعا ما من الشمس وعلى الرغم من ذلك فهو أكثر ضياء من الشمس وتبلغ كتلته 3 أضعاف كتلة الشمس ونصف قطره حوالي 17 ضعف من نصف قطر الشمس. وهذا النجم انهى مرحلة النسق الأساسي وفي طريقه للتطور إلى مرحلة عملاق أحمر.
يبلغ قدره الظاهري 2.04 ويبعد 96 سنة ضوئية عن الأرض[12]

اما الضفدع الثاني فيسمى أيضا فم الحوت.
انظر أيضا[عدل]
المراجع[عدل]
- ^ أ ب ت ث van Leeuwen، F. (نوفمبر 2007). "Validation of the new Hipparcos reduction". Astronomy and Astrophysics. ج. 474 ع. 2: 653–664. arXiv:0708.1752. Bibcode:2007A&A...474..653V. DOI:10.1051/0004-6361:20078357.
- ^ أ ب ت Johnson، H. L.؛ وآخرون (1966)، "UBVRIJKL photometry of the bright stars"، Communications of the Lunar and Planetary Laboratory، ج. 4، ص. 99، Bibcode:1966CoLPL...4...99J
- ^ Montes، D.؛ وآخرون (نوفمبر 2001)، "Late-type members of young stellar kinematic groups - I. Single stars"، Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society، ج. 328، ص. 45–63، arXiv:astro-ph/0106537، Bibcode:2001MNRAS.328...45M، DOI:10.1046/j.1365-8711.2001.04781.x
- ^ Wielen، R.؛ وآخرون (1999)، "Sixth Catalogue of Fundamental Stars (FK6). Part I. Basic fundamental stars with direct solutions"، Veröff. Astron. Rechen-Inst. Heidelb، Astronomisches Rechen-Institut Heidelberg، ج. 35، Bibcode:1999VeARI..35....1W
- ^ Elgarøy، Øystein؛ Engvold، Oddbjørn؛ Lund، Niels (مارس 1999)، "The Wilson-Bappu effect of the MgII K line - dependence on stellar temperature, activity and metallicity"، Astronomy and Astrophysics، ج. 343، ص. 222–228، Bibcode:1999A&A...343..222E
- ^ Sägesser، S. N.؛ Jordan، C. (مارس 2005). "Emission measures for the single giant β Ceti". في Favata، F.؛ Hussain، G. A. J.؛ Battrick، B. (المحررون). Proceedings of the 13th Cambridge Workshop on Cool Stars, Stellar Systems and the Sun, held 5-9 July, 2004 in Hamburg, Germany. European Space Agency. ص. 931. Bibcode:2005ESASP.560..931S.
- ^ أ ب Berio، P.؛ وآخرون (نوفمبر 2011)، "Chromosphere of K giant stars. Geometrical extent and spatial structure detection"، Astronomy & Astrophysics، ج. 535، ص. A59، arXiv:1109.5476، Bibcode:2011A&A...535A..59B، DOI:10.1051/0004-6361/201117479
- ^ أ ب ت Massarotti، Alessandro؛ وآخرون (يناير 2008). "Rotational and Radial Velocities for a Sample of 761 HIPPARCOS Giants and the Role of Binarity". The Astronomical Journal. ج. 135 ع. 1: 209–231. Bibcode:2008AJ....135..209M. DOI:10.1088/0004-6256/135/1/209.
- ^ 6695 "Bright Star Catalogue, 5th Revised Ed. (Hoffleit+, 1991)". فيزير . Centre de Données astronomiques de Strasbourg. مؤرشف من الأصل في 2018-01-23. اطلع عليه بتاريخ 2010-09-30.
{{استشهاد ويب}}: تحقق من قيمة|مسار أرشيف=(مساعدة)صيانة الاستشهاد: علامات ترقيم زائدة (link) - ^ "Beta Ceti: Giant Star's Corona Brightens with Age". Chandra Photo Album. Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics. 20 فبراير 2009. مؤرشف من الأصل في 2018-10-08. اطلع عليه بتاريخ 2011-12-28.
- ^ "bet Cet -- Variable Star". SIMBAD. Centre de Données astronomiques de Strasbourg. مؤرشف من الأصل في 2017-11-07. اطلع عليه بتاريخ 2010-09-30.
- ^ van Leeuwen, F. (2007). "HIP 3419". Hipparcos, the New Reduction. مؤرشف من الأصل في 2019-12-11. اطلع عليه بتاريخ 2010-08-22.