الساعد (نجم)
| الساعد | |
|---|---|
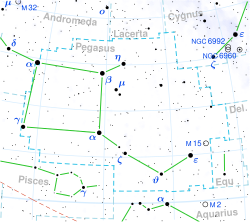
موقع الساعد الدائرة الحمراء(β)
| |
| معلومات الرصد حقبة J2000 اعتدالان J2000 |
|
| كوكبة | الفرس الأعظم |
| مطلع مستقيم | 23سا 03د 46.45746ث[1] |
| الميل | +28° 04′ 58.0336″[1] |
| القدر الظاهري (V) | 2.42[2] (2.31 - 2.74[3] |
| الخصائص | |
| نوع الطيف | M2.5II–IIIe[4] |
| U−B مؤشر اللون | +1.96[2] |
| B−V مؤشر اللون | +1.67[2] |
| نوع التغير | نجم متغير شبة منتظم[5] |
| القياسات الفلكية | |
| السرعة الشعاعية (Rv) | +8.7[6] كم/ث |
| الحركة الخاصة (μ) | +187.65[1]+136.93[1] |
| التزيح (π) | 16.64 ± 0.15 د.ق |
| البعد | 196 ± 2 س.ض (60٫1 ± 0٫5 ف.ف) |
| القدر المطلق (MV) | -1.49 |
| تفاصيل | |
| كتلة | 2.1[7] ك☉ |
| نصف قطر | 95[8] نق☉ |
| جاذبية سطحية (log g) | 1.20[9] سم.غ.ثا |
| درجة الحرارة | 3,689[9] ك |
| معدنية [Fe/H] | –0.11[9] dex |
| سرعة الدوران (v sin i) | 9.7[10] كم/ثا |
| تسميات اخرى | |
| Scheat, 53 Peg, HR 8775, BD +27°4480, HD 217906, SAO 90981, FK5 870, هيباركوس 113881.[4] | |
| قاعدة بيانات المراجع | |
| سيمباد | بيانات |
| تعديل مصدري - تعديل | |
أو بيتا الفرس الأعظم Beta Pegasi اسمه التقليدي Scheat مشتق من الاسم العربي وهو نجم في كوكبة الفرس الأعظم
يعتبر الساعد نجم لامع نسبيا مقارنة مع درجة حرارة سطحه التي تعتبر باردة نسبيا التي تصل إلى 3700 درجة كلفن وهو عملاق أحمر وأكبر من الشمس ب 95 مرة وضياءه ب 1500 مرة من الشمس .[8] ويتغير القدر الظاهري ما بين 2.31 + إلى 2.74+ .[3]
انظر أيضا[عدل]
المراجع[عدل]
- ^ أ ب ت ث van Leeuwen، F. (نوفمبر 2007)، "Validation of the new Hipparcos reduction"، Astronomy and Astrophysics، ج. 474، ص. 653–664، arXiv:0708.1752، Bibcode:2007A&A...474..653V، DOI:10.1051/0004-6361:20078357
- ^ أ ب ت Johnson، H. L.؛ وآخرون (1966). "UBVRIJKL photometry of the bright stars". Communications of the Lunar and Planetary Laboratory. ج. 4 ع. 99: 99. Bibcode:1966CoLPL...4...99J.
- ^ أ ب "Query= bet Peg". فهرس النجوم المتغيرة العام. Centre de Données astronomiques de Strasbourg. مؤرشف من الأصل في 2018-12-15. اطلع عليه بتاريخ 2010-01-05.
- ^ أ ب "V* bet Peg -- Pulsating variable Star"، سيمباد، Centre de Données astronomiques de Strasbourg، مؤرشف من الأصل في 2016-03-26، اطلع عليه بتاريخ 2010-01-05
- ^ Tabur، V.؛ وآخرون (ديسمبر 2009)، "Long-term photometry and periods for 261 nearby pulsating M giants"، Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society، ج. 400، ص. 1945–1961، arXiv:0908.3228، Bibcode:2009MNRAS.400.1945T، DOI:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2009.15588.x
- ^ Wilson، Ralph Elmer (1953)، "General Catalogue of Stellar Radial Velocities"، Washington، Washington: Carnegie Institution of Washington، Bibcode:1953QB901.W495.....
- ^ Tsuji، Takashi (مايو 2007). "Isotopic abundances of Carbon and Oxygen in Oxygen-rich giant stars". في Kupka، F.؛ Roxburgh، I.؛ Chan، K. (المحررون). Convection in Astrophysics, Proceedings of IAU Symposium #239 held 21-25 August, 2006 in Prague, Czech Republic. Proceedings of the International Astronomical Union. ج. 2. ص. 307–310. arXiv:astro-ph/0610180. Bibcode:2007IAUS..239..307T. DOI:10.1017/S1743921307000622.
- ^ أ ب James B. Kaler (22 مايو 2009). "SCHEAT (Beta Pegasi)". Stars. مؤرشف من الأصل في 2016-05-07. اطلع عليه بتاريخ 2010-01-05.
- ^ أ ب ت Soubiran، C.؛ وآخرون (2008)، "Vertical distribution of Galactic disk stars. IV. AMR and AVR from clump giants"، Astronomy and Astrophysics، ج. 480، ص. 91–101، arXiv:0712.1370، Bibcode:2008A&A...480...91S، DOI:10.1051/0004-6361:20078788
- ^ Massarotti، Alessandro؛ وآخرون (يناير 2008)، "Rotational and Radial Velocities for a Sample of 761 HIPPARCOS Giants and the Role of Binarity"، The Astronomical Journal، ج. 135، ص. 209–231، Bibcode:2008AJ....135..209M، DOI:10.1088/0004-6256/135/1/209