الدجاجة X-1: الفرق بين النسختين
| [نسخة منشورة] | [نسخة منشورة] |
ط بوت التصانیف المعادلة (25) +ترتيب (8.6): + تصنيف:ثنائي أشعة إكس |
Mr.Ibrahembot (نقاش | مساهمات) ط بوت: تعريب |
||
| سطر 9: | سطر 9: | ||
| حقبة =J2000 |
| حقبة =J2000 |
||
| المطلع_المستقيم ={{RA|19|58|21.67595}}<ref name=aaa474_2_653/> |
| المطلع_المستقيم ={{RA|19|58|21.67595}}<ref name=aaa474_2_653/> |
||
| الميل ={{ |
| الميل ={{ميل|+35|12|05.7783}}<ref name=aaa474_2_653/> |
||
| القدر_الظاهري =8.95<ref name=SIMBAD/> |
| القدر_الظاهري =8.95<ref name=SIMBAD/> |
||
| الكوكبة =[[ |
| الكوكبة =[[الدجاجة (كوكبة)|الدجاجة]]}} |
||
{{صندوق خصائص نجم |
{{صندوق خصائص نجم |
||
| التصنيف =O9.7Iab<ref name=SIMBAD/> |
| التصنيف =O9.7Iab<ref name=SIMBAD/> |
||
| سطر 37: | سطر 37: | ||
}} |
}} |
||
{{صندوق فهرس نجم |
{{صندوق فهرس نجم |
||
| تسميات =[[Astronomische Gesellschaft Katalog|AG (or AGK2)]]+35 1910, [[ |
| تسميات =[[Astronomische Gesellschaft Katalog|AG (or AGK2)]]+35 1910, [[مسح بون الفلكي]]+34 3815, [[فهرس هنري درابر]] 226868, [[هيباركوس]] 98298, [[Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory|SAO]] 69181, V1357 Cyg.<ref name=SIMBAD/> |
||
}} |
}} |
||
{{نهاية صندوق نجم}} |
{{نهاية صندوق نجم}} |
||
| سطر 75: | سطر 75: | ||
== المصادر == |
== المصادر == |
||
{{مراجع|2|refs=<ref name=aaa474_2_653>{{ |
{{مراجع|2|refs=<ref name=aaa474_2_653>{{Citation| last1=van Leeuwen | first1=F. | title=Validation of the new Hipparcos reduction | journal=Astronomy and Astrophysics | volume=474 | issue=2 | pages=653–664 |date=November 2007 | doi=10.1051/0004-6361:20078357 | bibcode=2007A&A...474..653V |arxiv = 0708.1752}}</ref><ref name=SIMBAD>{{Citation| author=Staff | date=March 3, 2003 | url=http://simbad.u-strasbg.fr/simbad/sim-id?protocol=html&Ident=HDE+226868 | title=V* V1357 Cyg -- High Mass X-ray Binary | publisher=Centre de Données astronomiques de Strasbourg | accessdate=2008-03-03}}</ref><ref name=lob647>{{Citation|display-authors=1 | last1=Bregman | first1=J. | last2=Butler | first2=D. | last3=Kemper | first3=E. | last4=Koski | first4=A. | last5=Kraft | first5=R. P. | last6=Stone | first6=R. P. S. | title=Colors, magnitudes, spectral types and distances for stars in the field of the X-ray source Cyg X-1 | journal=Lick Observatory Bulletin | date=1973 | pages=1 | volume=647 | bibcode=1973LicOB..24....1B}}</ref><ref name=apj321>{{Citation| last=Ninkov | first=Z. | last2=Walker | first2=G. A. H. | last3=Yang | first3=S. | title=The primary orbit and the absorption lines of HDE 226868 (Cygnus X-1) | journal=Astrophysical Journal | date=1987 | volume=321 | pages=425–437 | bibcode=1987ApJ...321..425N | doi=10.1086/165641}}</ref><ref name=orosz2011>{{Citation|last=Orosz |first=Jerome |date=December 1, 2011 |journal=The Astrophysical Journal |volume=742 |issue=2 |pages=84 |title=The Mass of the Black Hole In Cygnux X-1 |doi=10.1088/0004-637X/742/2/84|arxiv = 1106.3689 |bibcode = 2011ApJ...742...84O}}</ref><ref name=MNRAS358_3_851>{{Citation| last=Ziółkowski | first=J. | title=Evolutionary constraints on the masses of the components of HDE 226868/Cyg X-1 binary system | journal=Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society | date=2005 | volume=358 | issue=3 | pages=851–859 | arxiv=astro-ph/0501102 | doi=10.1111/j.1365-2966.2005.08796.x | bibcode=2005MNRAS.358..851Z}} Note: for radius and luminosity, see Table 1 with ''d''=2 kpc.</ref><ref name=hadrava>{{Citation| first1=Petr | last1=Hadrava | title=Optical spectroscopy of Cyg X-1 | journal=Proceedings of RAGtime 8/9: Workshops on black holes and neutron stars | pages=71 | date=September 15–21, 2007 | location=Opava, Czech Republic | arxiv=0710.0758 |bibcode = 2007ragt.meet...71H}}</ref><ref name=eas030610>{{Citation| author=Staff | date=June 10, 2003 | url=http://sci.esa.int/integral/32700-integral-s-view-of-cygnus-x-1/ | title=Integral's view of Cygnus X-1 | publisher=ESA | accessdate=2008-03-20}}</ref><ref name=science300_5622_1119>{{Citation| last1=Mirabel | first1=I. Félix | last2=Rodrigues | first2=Irapuan | title=Formation of a Black Hole in the Dark | journal=Science | date=2003 | volume=300 | issue=5622 | pages=1119–1120 | doi=10.1126/science.1083451 | pmid=12714674 | arxiv = astro-ph/0305205 | bibcode = 2003Sci...300.1119M}}</ref> |
||
}} |
}} |
||
نسخة 15:47، 6 أبريل 2017
| نجم الدجاجة إكس-1 | |
|---|---|
مكان النجم في كوكبة الدجاجة (النقطة الحمراء).
| |
| معلومات الرصد حقبة J2000 اعتدالان J2000 |
|
| كوكبة | الدجاجة |
| مطلع مستقيم | 19سا 58د 21.67595ث[1] |
| الميل | +35° 12′ 05.7783″[1] |
| القدر الظاهري (V) | 8.95[2] |
| الخصائص | |
| نوع الطيف | O9.7Iab[2] |
| U−B مؤشر اللون | −0.30[3] |
| B−V مؤشر اللون | +0.81[3] |
| نوع التغير | متغير بيضاوي دوار |
| القياسات الفلكية | |
| السرعة الشعاعية (Rv) | −13[2] كم/ث |
| الحركة الخاصة (μ) | −3.37[1]−7.15[1] |
| التزيح (π) | 0.539 ± 0.033 د.ق |
| البعد | 6٬100 ± 400 س.ض (1٬900 ± 100 ف.ف) |
| القدر المطلق (MV) | −6.5±0.2[4] |
| تفاصيل | |
| كتلة | 14–16[5] ك☉ |
| نصف قطر | 20–22[6] نق☉ |
| إضاءة | 3–4×105[6] ض☉ |
| جاذبية سطحية (log g) | 3.31±0.07[7] سم.غ.ثا |
| درجة الحرارة | 31000[8] ك |
| دوران | every 5.6 days |
| عمر | 5 million[9] سنة |
| تسميات اخرى | |
| AG (or AGK2)+35 1910, مسح بون الفلكي+34 3815, فهرس هنري درابر 226868, هيباركوس 98298, SAO 69181, V1357 Cyg.[2] | |
| تعديل مصدري - تعديل | |
نجم الدجاجة اكس-1 (Cygnus X-1) هو مصدر للأشعة السينية متواجد في كوكبة الدجاجة. اكتُشف سنة 1965 بالأقمار الصناعية التي سجلت الأشعة السينية القادمة من الفضاء الخارجي، وعلى الأخص من هذا النجم الذي لا يُرى بالتلسكوبات الضوئية برغم أنه يقع في مجرتنا.
طبيعته
وكما يتضح من اسم هذا النجم فهو من أوائل مصادر الأشعة السينية التي تم اكتشافها. واستطاع علماء الفلك في عام 1969 معرفة المزيد عن هذا النجم الغامض (الدجاجة اكس- 1) فقد تغيرت قوة نبضات الأشعة السينية التي تصدر منه.
وفي عامي 1971 1972 حدث تطور هام في رصد هذا النجم. فخلال شهري مارس وأبريل 1971 اكتشف القمر الصناعي (أوهورو) نقصا ملحوظا في قوة إصدار الأشعة السينية من نجم الدجاجة اكس- 1 وظهر فجأة مصدر للأشعة الراديوية في نفس مكان هذا النجم الغامض. واستخدمت أقوى التلسكوبات الراديوية في البحث عن هذا المصدر الراديوي ولكن دون جدوى ثم اتضح فيما بعد أمر غريب إن كلا من الأشعة السينية والموجات الراديوية تنبعثان من نفس المصدر. وأهمية هذا الاكتشاف تكمن في أن الموجات الراديوية يمكن قياسها بدرجة أدق من الأشعة السينية. وبهذا تم التأكد بأن نجما هائلا آخرا يدور حول المصدر (الدجاجة اكس- 1) وأن الإثنين يشكلان مزدوجا يدوران حول بعضهما في دورة تستغرق نحو 6 أيام. وقد قـُدرت المسافة بينهما بنحو 30 مليون كيلومتر (أي نحو 20 % من المسافة بين الأرض والشمس). واستطاع العلماء بواسطة التحليل الطيفي معرفة الكثير عن هذا النجم التابع الذي أطلق عليه اسم (HDE 226868) وهو الرقم الذي وضعه له العالم هنري درابر في فهرس التصنيف الطيفي. وهذا النجم الهائل من المرتبة الطيفية الساخنة ولونه أزرق ويقع في مجموعة الدجاجة Cygnus ويبعد عنا بحوالي 6500 سنة ضوئية.
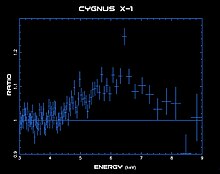
وفي عا 1971 اكتشف علماء الفلك في اليابان أن الأشعة السينية من المصدر الخفي (الدجاجة اكس- 1) تخفق بسرعة كبيرة جدا وهذا يعني أن هذا المصدر الذي يرسل الأشعة السينية كثافته عالية جدا ومن ثم فقد زاد احتمال أن يكون النجم الدجاجة اكس- 1. ثقب أسود تصل كتلته نحو 7 أضعاف كتلة الشمس. كما توصل العلماء إلى تقدير كتلة التابع (HDE 226868) وقدروها بنحو 22 مرة كتلة الشمس. ويعزى اصدار أشعة أكس إلى أن الثقب الأسود يسحب الغلاف الغازي الخارجي ل (HDE 226868) فتنهار عليه بسرعة كبيرة جدا وترتفع درجة حرارتها فتنتج اشعة إكس. ويبين البياني توزيع طيف الأشعة السينية القادمة من الدجاجة اكس-1 وهو يمتد بين 3 و 9 كيلوإلكترون فولت keV ويتميز التوزيع بقمة عند نحو 6 keV. ويبين الرسم التخيلي لأحد الفنانين كيف يسحب الثقب الأسود الغاز من النجم المجاور له (HDE 226868). واستمر علماء التحليل الطيفي عملهم وبحثوا عن آثار ل انزياح دوبلر في طيف النجم الهائل (HDE 226868) واتضح لهم أنه يدور مدفوعا بقوة ثقالة (جاذبية) جبارة لرفيق خفي هو الدجاجة اكس- 1.
اقرأ أيضا
- علم الفلك للأشعة السينية
- في 404 الدجاجة
- نجم-أو
- ثنائي أشعة إكس
- سكوربيوس إكس-1
- ثقب أسود
- نجم نيوتروني
- قزم أبيض
- تخليق العناصر
- مستعر أعظم
- انفجار أشعة غاما 080913
- انفجار أشعة غاما 080319ب
- انفجار أشعة غاما 971214
- انفجار أشعة غاما 080916C
- انفجار أشعة غاما 060218
- مستعر أعظم II
- مستعر أعظم نوع Ia
- مستعر أعظم
المصادر
- ^ أ ب ت ث van Leeuwen، F. (نوفمبر 2007)، "Validation of the new Hipparcos reduction"، Astronomy and Astrophysics، ج. 474 ع. 2: 653–664، arXiv:0708.1752، Bibcode:2007A&A...474..653V، DOI:10.1051/0004-6361:20078357
- ^ أ ب ت ث Staff (3 مارس 2003)، V* V1357 Cyg -- High Mass X-ray Binary، Centre de Données astronomiques de Strasbourg، اطلع عليه بتاريخ 2008-03-03
- ^ أ ب Bregman، J.؛ وآخرون (1973)، "Colors, magnitudes, spectral types and distances for stars in the field of the X-ray source Cyg X-1"، Lick Observatory Bulletin، ج. 647: 1، Bibcode:1973LicOB..24....1B
- ^ Ninkov، Z.؛ Walker، G. A. H.؛ Yang، S. (1987)، "The primary orbit and the absorption lines of HDE 226868 (Cygnus X-1)"، Astrophysical Journal، ج. 321: 425–437، Bibcode:1987ApJ...321..425N، DOI:10.1086/165641
- ^ Orosz، Jerome (1 ديسمبر 2011)، "The Mass of the Black Hole In Cygnux X-1"، The Astrophysical Journal، ج. 742 ع. 2: 84، arXiv:1106.3689، Bibcode:2011ApJ...742...84O، DOI:10.1088/0004-637X/742/2/84
- ^ أ ب Ziółkowski، J. (2005)، "Evolutionary constraints on the masses of the components of HDE 226868/Cyg X-1 binary system"، Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society، ج. 358 ع. 3: 851–859، arXiv:astro-ph/0501102، Bibcode:2005MNRAS.358..851Z، DOI:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2005.08796.x Note: for radius and luminosity, see Table 1 with d=2 kpc.
- ^ Hadrava، Petr (15–21 سبتمبر 2007)، "Optical spectroscopy of Cyg X-1"، Proceedings of RAGtime 8/9: Workshops on black holes and neutron stars، Opava, Czech Republic: 71، arXiv:0710.0758، Bibcode:2007ragt.meet...71H
- ^ Staff (10 يونيو 2003)، Integral's view of Cygnus X-1، ESA، اطلع عليه بتاريخ 2008-03-20
- ^ Mirabel، I. Félix؛ Rodrigues، Irapuan (2003)، "Formation of a Black Hole in the Dark"، Science، ج. 300 ع. 5622: 1119–1120، arXiv:astro-ph/0305205، Bibcode:2003Sci...300.1119M، DOI:10.1126/science.1083451، PMID:12714674
- الكون والثقوب السوداء - رؤوف وصفي.
| في كومنز صور وملفات عن: الدجاجة X-1 |


