قائمة المجرات القمرية لمجرة درب التبانة
قائمة المجرات القمرية لمجرة درب التبانة المجرات التابعة أو المجرات القمرية وفي الغالب تكون مجرات صغيرة أو قزمة وبالتالي لا مفر من أن تقع تحت تأثير حقل الجاذبية لمجرات أخرى أكبر حجماً، حيث تدور حولها بطريقة مشابهة لطريقة دوران القمر حول الأرض. المجرات القمربة لمجرة درب التبانة جزء من مجموعة درب التبانة الفرعية التي بدورها جزء من المجموعة المحلية.[1]
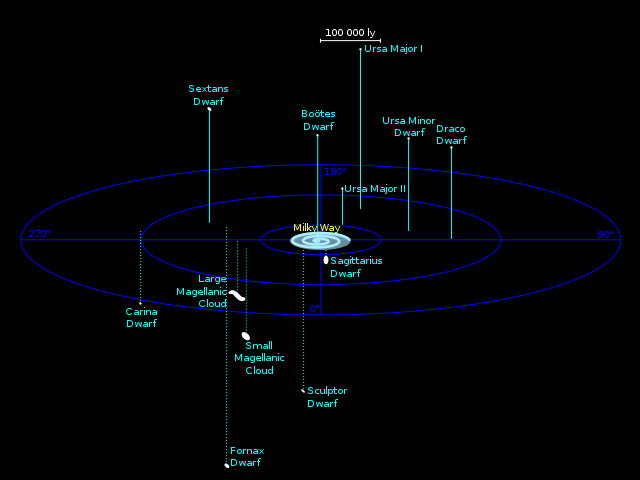
هناك 57 مجرة صغيرة مؤكدة تقع ضمن 420 الف فرسخ فلكي (1.4 مليون سنة ضوئية) من درب التبانة، ولكن ليس كلها بالضرورة في مدار حول درب التبانة، وبعضها قد يكون في مدار حول مجرات أخرى. المجرات الوحيدة التي تشاهد باللعين المجردة هي سحابتا ماجلان الكبرى والصغرى (طالع:قائمة المجرات المرئية)، وتشير القياسات التي أجريت باستخدام مرصد هابل الفضائي في عام 2006 إلى أن السحب الماجلانية تتحرك بسرعة كبيرة لكي تكون في مدار حول درب التبانة.[2]
القائمة[عدل]
وتشمل المجرات التابعة لمجرتنا درب التبانة ما يلي:[3]
| اسم المجرة | القطر (كيلو فرسخ فلكي) | البعد (كيلو فرسخ فلكي) |
قدر مطلق | النوع | تاريخ الإكتشاف |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| مجرة كانيس ميجور القزمة | 1.5 | 8 | Irr | 2003 | |
| مجرة الرامي الإهليجية القزمة | 2.6 | 20 | E | 1994 | |
| سحابة ماجلان الكبرى | 4 | 48.5 | SBm | عصر ما قبل التاريخ | |
| سحابة ماجلان الصغرى | 2 | 61 | Irr | عصر ما قبل التاريخ | |
| مجرة الدب الأكبر الثانية القزمة | 0.2 | 30 | dG D | 2006 | |
| مجرة الدب الأصغر القزمة | 0.4 | 60 | dE4 | 1954 | |
| مجرة التنين القزمة | 0.7 | 80 | dE0 | 1954 | |
| مجرة النحات القزمة | 0.8 | 90 | dE3 | 1937 | |
| مجرة السدس القزمة | 0.5 | 90 | dE3 | 1990 | |
| قزمة القاعدة البيضاوية | 0.5 | 100 | dE3 | 1977 | |
| قزمة الدب الأكبر الأولى | - | 100 | dG D | 2005 | |
| الكور القزمة | 0.6 | 140 | dE2 | 1938 | |
| الأسد القزمة II | 0.7 | 210 | dE0 | 1950 | |
| الأسد القزمة I | 0.5 | 250 | dE3 | 1950 | |
| قزمة الأسد الرابعة | 0.3 | 160 | dSph | 2006 | |
| قزمة الأسد الخامسة | 0.08 | 180 | dSph | 2007 | |
| قزمة لأسد -T | 0.34 | 420 | dSph/dIrr | 2006 | |
| مجرة العواء القزمة | 0.3 | 60 | dSph | 2006 | |
| مجرة العواء القزمة II | 0.1 | 42 | dSph | 2007 | |
| مجرة العواء القزمة III | 1 | 46 | dSph? | 2009 | |
| مجرة الهلبة القزمة | 0.14 | 42 | dSph | 2006 | |
| Segue 1 | 0.06 | 23 | -3.0 | dSph | 2007 |
| Segue 2 | 0.07 | 35 | dSph | 2007 | |
| السلوقيان I | 2 | 220 | dSph | 2006 | |
| السلوقيان II | 0.3 | 155 | dSph | 2006 | |
| الجاثي القزمة | 0.7 | 135 | dSph | 2006 | |
| قزمة الحوت I | 80 | dSph? | 2009 | ||
| قزمة الحوت II | 0.12 | 180 | dSph | 2010 | |
| كأس الباطية I | 0.06 | 145 | GC[4] | 2014 [5][6] | |
| الشبكة II | - | 30 | dSph | 2015 [7][8] | |
| النهر II [9] | 0.55 | 366 | -7.1 | dSph | 2015 [7][8] |
| البندول I | - | 100 | dSph? | 2015 [7][8] | |
| المرسمة I | - | 115 | dSph? | 2015 [7][8] | |
| العنقاء II | - | 100 | dSph? | 2015 [7][8] | |
| الهندي I | - | 100 | GC | 2015 [7][8] | |
| الكركي I | - | 120 | dSph | 2015 [7] | |
| النهر III | - | 90 | dSph? | 2015 [7][8] | |
| الطوقان II | - | 70 | dSph | 2015 [7][8] | |
| المثلث II | 0.07 | 30 | -1.8 | dSph | 2015 |
| الشجاع II | 0.14 | 128 | dSph | 2015 [10] | |
| الفرس الأعظم III | 0.11 | 215 | -3.4 | dSph | 2015 [11][12] |
| الكركي II | 0.19 | 53 | dSph | 2015 [13] | |
| الطوقان III | 0.09 | 25 | dSph | 2015 [13] | |
| الحمامة I | 0.21 | 182 | dSph | 2015 [13] | |
| الطوقان IV | 0.25 | 48 | dSph | 2015 [13] | |
| الشبكة III | 0.13 | 92 | dSph | 2015 [13] | |
| الطوقان V | 0.03 | 55 | dSph | 2015 [13] | |
| الهندي II | 0.36 | 214 | dSph? | 2015 [13] | |
| قيطس II | 0.03 | 30 | dSph? | 2015 [13] | |
| البندول II | 0.09 | 78 | dSph | 2015 [14] | |
| التنين II | 0.04 | 20 | -2.9 | dSph | 2015 [15] |
| الرامي القزمة II | 0.08 | 67 | -5.2 | dSph | 2015 [15] |
| ديس 1 | - | 82 | GC | 2016 [16] | |
| كأس الباطية II | 2.2 | 117.5 | dSph | 2016 [17] | |
| مجرة الدلو 2 | 0.32 | 108 | -4.2 | dSph | 2016 [18] |
انظر أيضاً[عدل]
- قائمة المجرات المرئية
- قائمة المجرات المسماة
- المجموعة المحلية
- درب التبانة
- قائمة مجرات المجموعة المحلية
- قائمة مجموعات وعناقيد المجرات
مراجع[عدل]
- ^ David G. Turner (15 أغسطس 2013). "An Eclectic View of our Milky Way Galaxy". Canadian Journal of Physics (نُشِر في سبتمبر 2013). ج. 92 ع. 9: 959–963. arXiv:1310.0014. Bibcode:2014CaJPh..92..959T. DOI:10.1139/cjp-2013-0429.
- ^ "Press release: Magellanic Clouds May Be Just Passing Through". Harvard University. 9 يناير 2007. مؤرشف من الأصل في 2019-04-23.
- ^ Nils Sj?lander. "Milky Way Satellite Galaxies". مؤرشف من الأصل في 2014-02-19.
- ^ Voggel، Karina؛ Hilker، Michael؛ Baumgardt، Holger؛ Collins، Michelle L.M.؛ Grebel، Eva K.؛ Husemann، Bernd؛ Richtler، Tom؛ Frank، Matthias J. "Probing the boundary between star clusters and dwarf galaxies: A MUSE view on the dynamics of Crater/Laevens I". arXiv:1604.06806 [astro-ph].
- ^ Benjamin P. M. Laevens؛ وآخرون (8 أبريل 2014). "A NEW DISTANT MILKY WAY GLOBULAR CLUSTER IN THE PAN-STARRS1 3π SURVEY". The Astrophysical Journal Letters. ج. 786 ع. 1: L3. arXiv:1403.6593. Bibcode:2014ApJ...786L...3L. DOI:10.1088/2041-8205/786/1/L3.
- ^ V. Belokurov, M. J. Irwin, S. E. Koposov, N. W. Evans, E. Gonzalez-Solares, N. Metcalfe and T. Shanks (1 يوليو 2014). "ATLAS lifts the Cup: discovery of a new Milky Way satellite in Crater". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. ج. 441 ع. 3: 2124–2133. arXiv:1403.3406. Bibcode:2014MNRAS.441.2124B. DOI:10.1093/mnras/stu626.
{{استشهاد بدورية محكمة}}: صيانة الاستشهاد: أسماء متعددة: قائمة المؤلفين (link) - ^ أ ب ت ث ج ح خ د ذ Sergey E. Koposov؛ Vasily Belokurov؛ Gabriel Torrealba؛ N. Wyn Evans (10 مارس 2015). "Beasts of the Southern Wild. Discovery of a large number of Ultra Faint satellites in the vicinity of the Magellanic Clouds". The Astrophysical Journal. ج. 805: 130. arXiv:1503.02079. Bibcode:2015ApJ...805..130K. DOI:10.1088/0004-637X/805/2/130.
- ^ أ ب ت ث ج ح خ د DES Collaboration (10 مارس 2015). "Eight New Milky Way Companions Discovered in First-Year Dark Energy Survey Data". The Astrophysical Journal. ج. 807: 50. arXiv:1503.02584. Bibcode:2015ApJ...807...50B. DOI:10.1088/0004-637X/807/1/50.
- ^ Crnojevi?، D.؛ Sand، D. J.؛ Zaritsky، D.؛ Spekkens، K.؛ Willman، B.؛ Hargis، J. R. "DEEP IMAGING OF ERIDANUS II AND ITS LONE STAR CLUSTER". arXiv:1604.08590 [astro-ph].
- ^ Martin، Nicolas F.؛ وآخرون (Survey of the Magellanic Stellar History) (23 أبريل 2015). "HYDRA II: A FAINT AND COMPACT MILKY WAY DWARF GALAXY FOUND IN THE SURVEY OF THE MAGELLANIC STELLAR HISTORY". The Astrophysical Journal Letters. ج. 804 ع. 1: L5. arXiv:1503.06216. Bibcode:2015ApJ...804L...5M. DOI:10.1088/2041-8205/804/1/L5.
- ^ Kim، Dongwon؛ Jerjen، Helmut؛ Mackey، Dougal؛ Da Costa، Gary S.؛ Milone، Antonino P. (12 مايو 2015). "A HERO'S DARK HORSE: DISCOVERY OF AN ULTRA-FAINT MILKY WAY SATELLITE IN PEGASUS". The Astrophysical Journal Letters. ج. 804 ع. 2: L44. arXiv:1503.08268. DOI:10.1088/2041-8205/804/2/L44.
- ^ Kim، Dongwon؛ Jerjen، Helmut؛ Geha، Marla؛ Chiti، Anirudh؛ Milone، Antonino P.؛ Mackey، Dougal؛ da Costa، Gary؛ Frebel، Anna؛ Conn، Blair. "PORTRAIT OF A DARK HORSE: PHOTOMETRIC PROPERTIES AND KINEMATICS OF THE ULTRA-FAINT MILKY WAY SATELLITE PEGASUS III". arXiv:1608.04934 [astro-ph.GA].
- ^ أ ب ت ث ج ح خ د A. Drlica-Wagner؛ وآخرون (4 نوفمبر 2015). "Eight ultra-faint galaxy candidates discovered in Year Two of the Dark Energy Survey". The Astrophysical Journal. ج. 813 ع. 2: 109. arXiv:1508.03622. Bibcode:2015ApJ...813..109D. DOI:10.1088/0004-637X/813/2/109. مؤرشف من الأصل في 2019-06-16.
- ^ Dongwon Kim؛ Helmut Jerjen (28 يوليو 2015). "Horologium II: A second ultra-faint Milky Way satellite in the Horologium constellation". The Astrophysical Journal Letters. ج. 808 ع. 2: L39. arXiv:1505.04948. Bibcode:2015ApJ...808L..39K. DOI:10.1088/2041-8205/808/2/L39. مؤرشف من الأصل في 2019-12-12.
{{استشهاد بدورية محكمة}}:|archive-date=/|archive-url=timestamp mismatch (مساعدة) والوسيط غير المعروف|lastauthoramp=تم تجاهله يقترح استخدام|name-list-style=(مساعدة) - ^ أ ب Laevens، B.P.M؛ Martin، N.F.؛ Bernard، E.J.؛ Schlafly، E.F.؛ Sesar، B. (1 نوفمبر 2015). "SAGITTARIUS II, DRACO II AND LAEVENS 3: THREE NEW MILKY WAY SATELLITES DISCOVERED IN THE PAN-STARRS 1 3? SURVEY". The Astrophysical Journal. ج. 813 ع. 1. arXiv:1507.07564. DOI:10.1088/0004-637X/813/1/44.
- ^ E. Luque؛ وآخرون (9 فبراير 2016). "Digging deeper into Southern skies: a compact Milky Way companion discovered in first-year Dark Energy Survey data". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. ج. 458 ع. 1: 603–612. arXiv:1508.02381. Bibcode:2016MNRAS.458..603L. DOI:10.1093/mnras/stw302. مؤرشف من الأصل في 2020-03-14.
- ^ G. Torrealba, S.E. Koposov, V. Belokurov & M. Irwin (13 أبريل 2016). "The feeble giant. Discovery of a large and diffuse Milky Way dwarf galaxy in the constellation of Crater". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. Bibcode:2016MNRAS.tmp..635T. DOI:10.1093/mnras/stw733.
{{استشهاد بدورية محكمة}}: صيانة الاستشهاد: bibcode (link) صيانة الاستشهاد: أسماء متعددة: قائمة المؤلفين (link) - ^ Torrealba، G.؛ Koposov، S.E.؛ Belokurov، V.؛ Irwin، M.؛ Collins، M.؛ Spencer، M.؛ Ibata، R.؛ Matteo، M.؛ Bonaca، A.؛ Jethwa، P. "At the survey limits: discovery of the Aquarius 2 dwarf galaxy in the VST ATLAS and the SDSS data". arXiv:1605.05338 [astro-ph.GA].

